Introduction
Stress has quietly become a part of everyday life. Work pressure, financial worries, screen exposure, and lack of rest constantly keep the mind active. Over time, this stress does not stay limited to the mind—it starts affecting the heart, digestion, sleep, blood pressure, and immunity. Many people look for complicated solutions like supplements or medication, but one of the most powerful stress‑relief tools is something you already do every day: breathing.
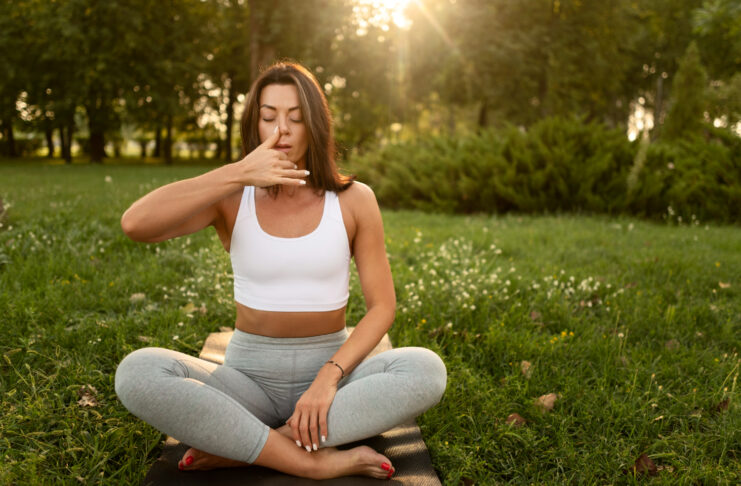
Most people breathe shallowly without realizing it. A simple habit of deep, controlled breathing can naturally calm the nervous system, reduce stress hormones, improve heart health, and bring mental clarity. When practiced daily, deep breathing becomes a natural medicine for both mind and body.
Why Stress Harms the Body
• Stress keeps the nervous system overactive
Continuous stress keeps the body in “fight or flight” mode, increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
• Stress increases harmful hormones
High cortisol levels disturb sleep, digestion, weight control, and immunity.
• Stress affects heart health
Long‑term stress increases the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease.
• Stress reduces oxygen supply
Shallow breathing limits oxygen flow to organs and muscles.
How Deep Breathing Affects Your Body
• It calms the nervous system
Deep breathing activates the relaxation response and reduces anxiety.
• It lowers heart rate and blood pressure
Slow breathing reduces strain on the heart.
• It improves oxygen delivery
More oxygen reaches the brain, heart, and muscles.
• It balances stress hormones
Cortisol levels reduce naturally.
• It improves focus and mental clarity
A calm mind works more efficiently.
• It supports better sleep
Relaxed breathing prepares the body for rest.
Natural Benefits You Will Notice
• Reduced stress and anxiety
• Calmer mind and emotions
• Improved heart rhythm
• Better concentration
• Reduced headaches and tension
• Better digestion
• Deeper and more restful sleep
Correct Way to Practice Deep Breathing
• Sit or lie down comfortably
Keep your spine relaxed and straight.
• Breathe in slowly through your nose
Let your belly expand instead of your chest.
• Hold the breath briefly
A short pause helps oxygen absorption.
• Exhale slowly through your mouth
Release tension with the breath.
• Practice for 5 to 10 minutes daily
Consistency gives the best results.
Best Time to Do Deep Breathing
• Morning to start the day calmly
• During stressful moments
• Before sleeping to improve sleep quality
• After work to relax the mind
Common Mistakes to Avoid
• Breathing too fast
This can increase anxiety instead of reducing it.
• Lifting shoulders while breathing
This indicates shallow breathing.
• Practicing irregularly
Daily practice is essential for benefits.
• Forcing the breath
Breathing should be gentle and comfortable.
Final Thoughts
You don’t need medication or expensive therapies to calm your mind and protect your heart. A simple daily deep breathing habit can naturally reduce stress, balance emotions, improve heart health, and bring inner calm. Just a few minutes of conscious breathing each day can create long‑lasting changes in your mental and physical well‑being.
Trusted Medical Sources
• Cleveland Clinic – Deep Breathing and Stress